VCE Maths Methods Integral Calculus Mini Test 6
Number of marks: 10
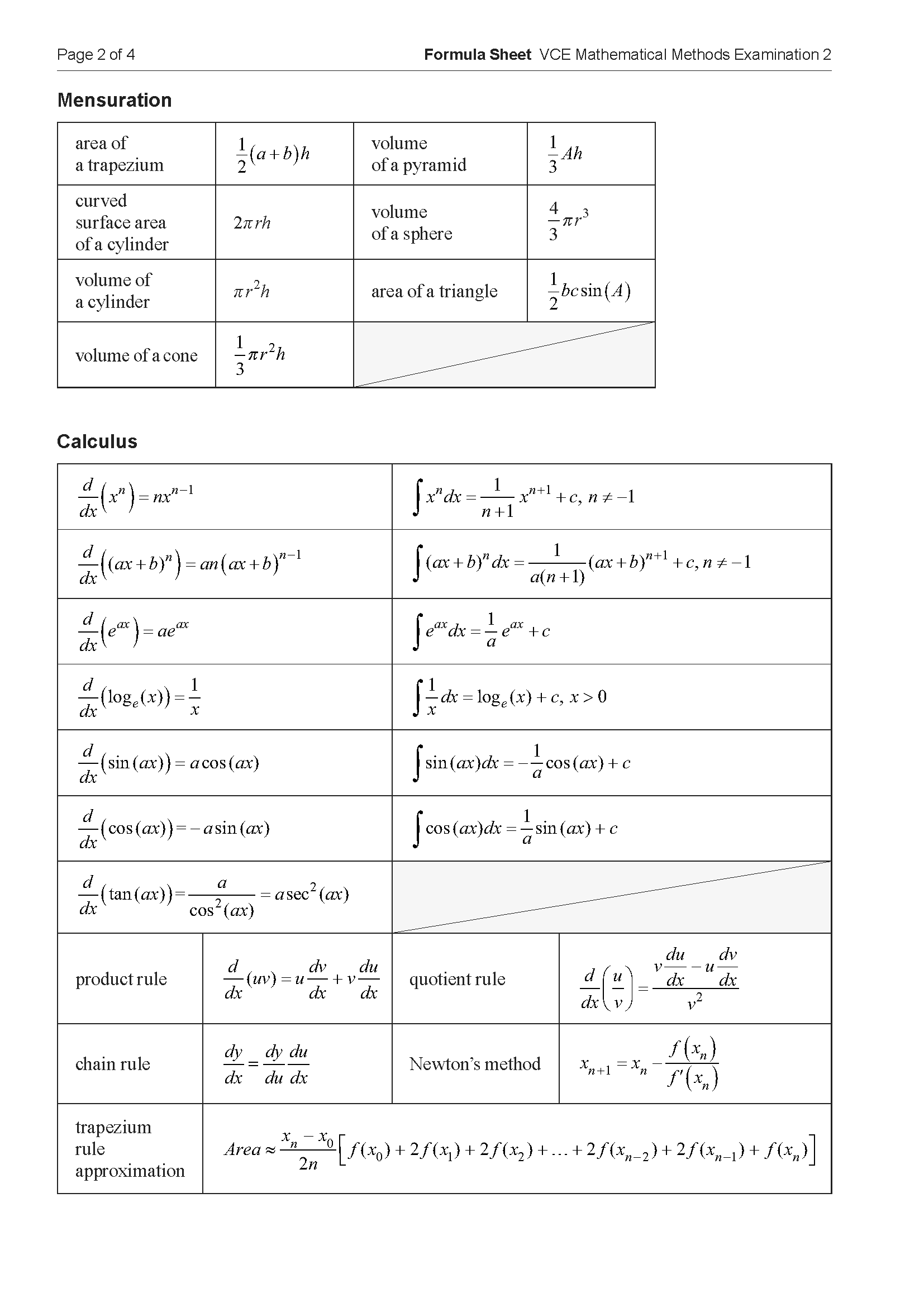
Reading time: 2 minutes
Writing time: 15 minutes
Section A – Calculator Allowed
Instructions
• Answer all questions in pencil on your Multiple-Choice Answer Sheet.
• Choose the response that is correct for the question.
• A correct answer scores 1; an incorrect answer scores 0.
• Marks will not be deducted for incorrect answers.
• No marks will be given if more than one answer is completed for any question.
• Unless otherwise indicated, the diagrams in this book are not drawn to scale.
\(\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{3}} (a\sin(x) + b\cos(x))dx\) is equal to
- A. \(\frac{(2-\sqrt{3})a-b}{2}\)
- B. \(\frac{b-(2-\sqrt{3})a}{2}\)
- C. \(\frac{(2-\sqrt{3})a+b}{2}\)
- D. \(\frac{(2-\sqrt{3})b-a}{2}\)
- E. \(\frac{(2-\sqrt{3})b+a}{2}\)
Let \(f'(x) = 3x^2 - 2x\) such that \(f(4) = 0\).
The rule of \(f\) is
- A. \(f(x) = x^3 - x^2\)
- B. \(f(x) = x^3 - x^2 + 48\)
- C. \(f(x) = x^3 - x^2 - 48\)
- D. \(f(x) = 6x - 2\)
- E. \(f(x) = 6x - 24\)
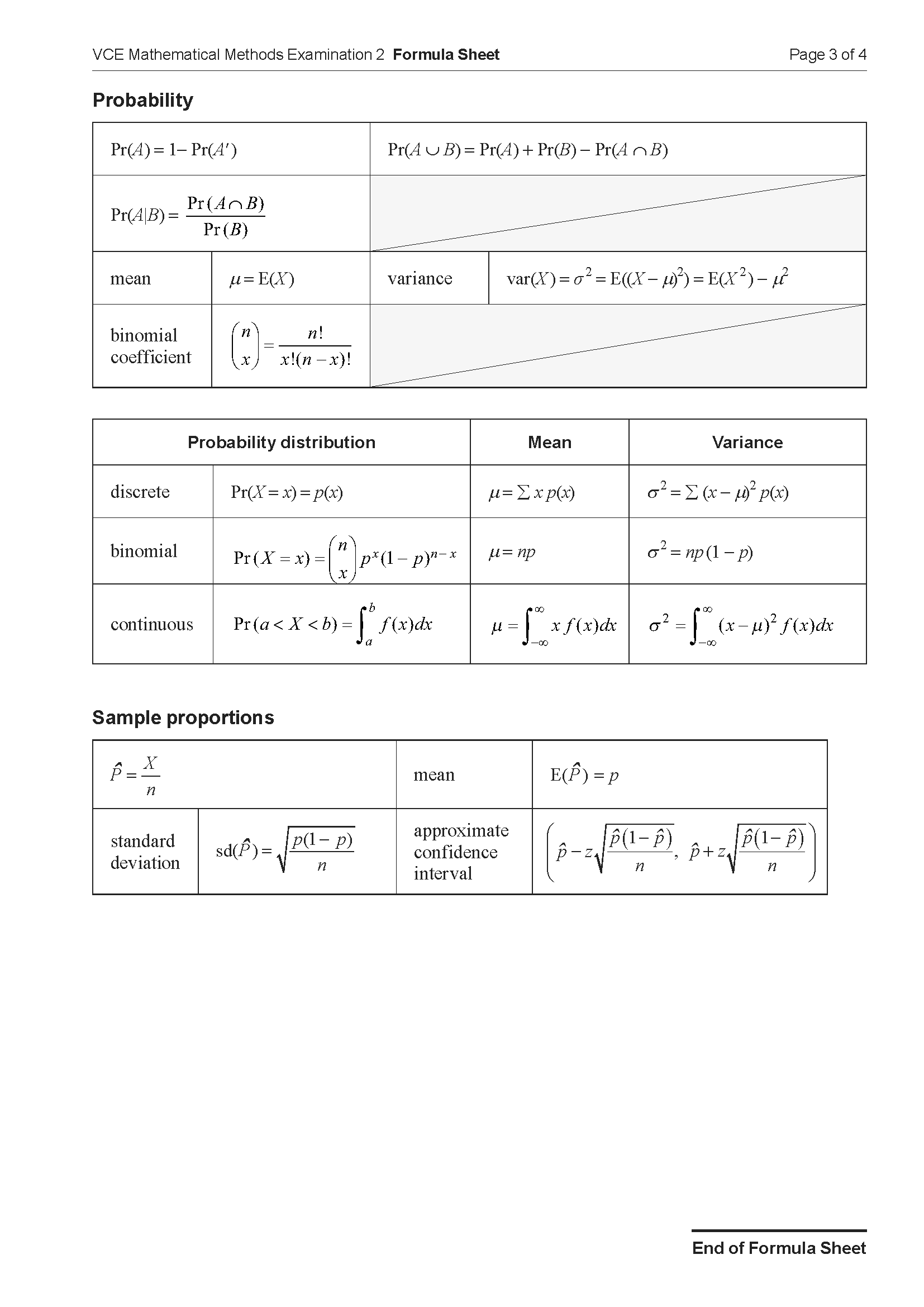
The graphs \(f: R \to R, f(x) = \cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right)\) and \(g: R \to R, g(x) = \sin(\pi x)\) are shown in the diagram below.
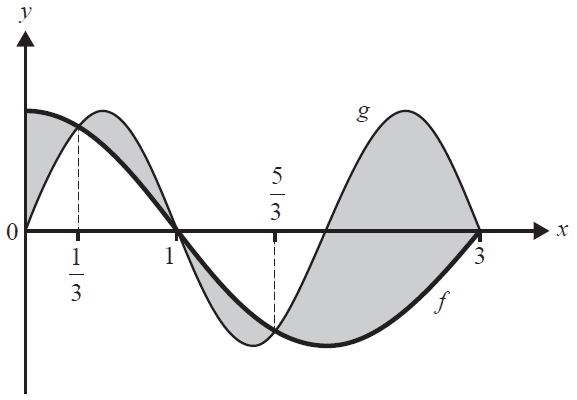
An integral expression that gives the total area of the shaded regions is
- A. \(\int_0^3 \left(\sin(\pi x) - \cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right)\right)dx\)
- B. \(2\int_\frac{5}{3}^{3} \left(\sin(\pi x) - \cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right)\right)dx\)
- C. \(\int_0^\frac{1}{3} \left(\cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right) - \sin(\pi x)\right)dx - 2\int_\frac{1}{3}^1 \left(\cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right) - \sin(\pi x)\right)dx - \int_\frac{5}{3}^3 \left(\cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right) - \sin(\pi x)\right)dx\)
- D. \(2\int_0^\frac{5}{3} \left(\cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right) - \sin(\pi x)\right)dx - 2\int_\frac{5}{3}^{3} \left(\cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right) - \sin(\pi x)\right)dx\)
- E. \(\int_0^\frac{1}{3} \left(\cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right) - \sin(\pi x)\right)dx + 2\int_\frac{1}{3}^1 \left(\sin(\pi x) - \cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right)\right)dx + \int_\frac{5}{3}^1 \left(\cos\left(\frac{\pi x}{2}\right) - \sin(\pi x)\right)dx\)
End of Section A
Section B – No Calculator
Instructions
• Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
• Write your responses in English.
• In questions where a numerical answer is required, an exact value must be given unless otherwise specified.
• In questions where more than one mark is available, appropriate working must be shown.
• Unless otherwise indicated, the diagrams in this book are not drawn to scale.
Let \( f'(x) = x^3 + x \).
Find \( f(x) \) given that \( f(1) = 2 \). 2 marks
Part of the graph of \(y = f(x)\) is shown below. The rule \(A(k) = k \sin(k)\) gives the area bounded by the graph of \(f\), the horizontal axis and the line \(x = k\).
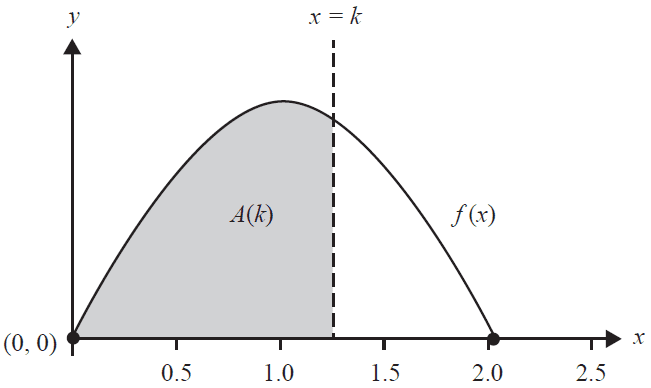
a. State the value of \( A\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right) \). 1 mark
b. Evaluate \( f\left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right) \). 2 marks
c. Consider the average value of the function \(f\) over the interval \(x \in [0, k]\), where \(k \in [0, 2]\). Find the value of \(k\) that results in the maximum average value. 2 marks
End of examination questions
VCE is a registered trademark of the VCAA. The VCAA does not endorse or make any warranties regarding this study resource. Past VCE exams and related content can be accessed directly at www.vcaa.vic.edu.au