2023 VCE Maths Methods Mini Test 2
Number of marks: 11
Reading time: 2 minutes
Writing time: 16 minutes
Section B – Calculator Allowed
Instructions
• Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
• Write your responses in English.
• In questions where a numerical answer is required, an exact value must be given unless otherwise specified.
• In questions where more than one mark is available, appropriate working must be shown.
• Unless otherwise indicated, the diagrams in this book are not drawn to scale.
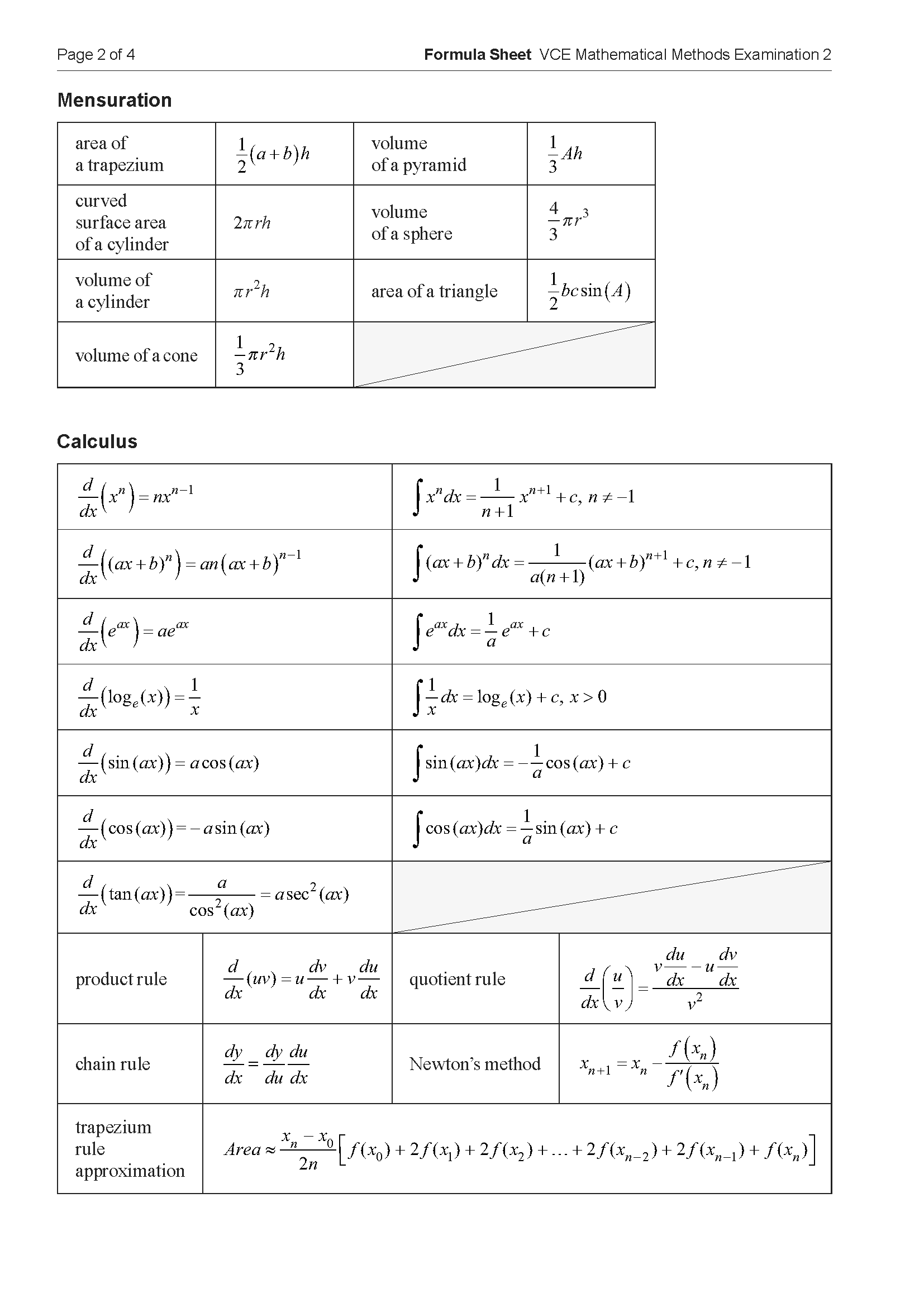
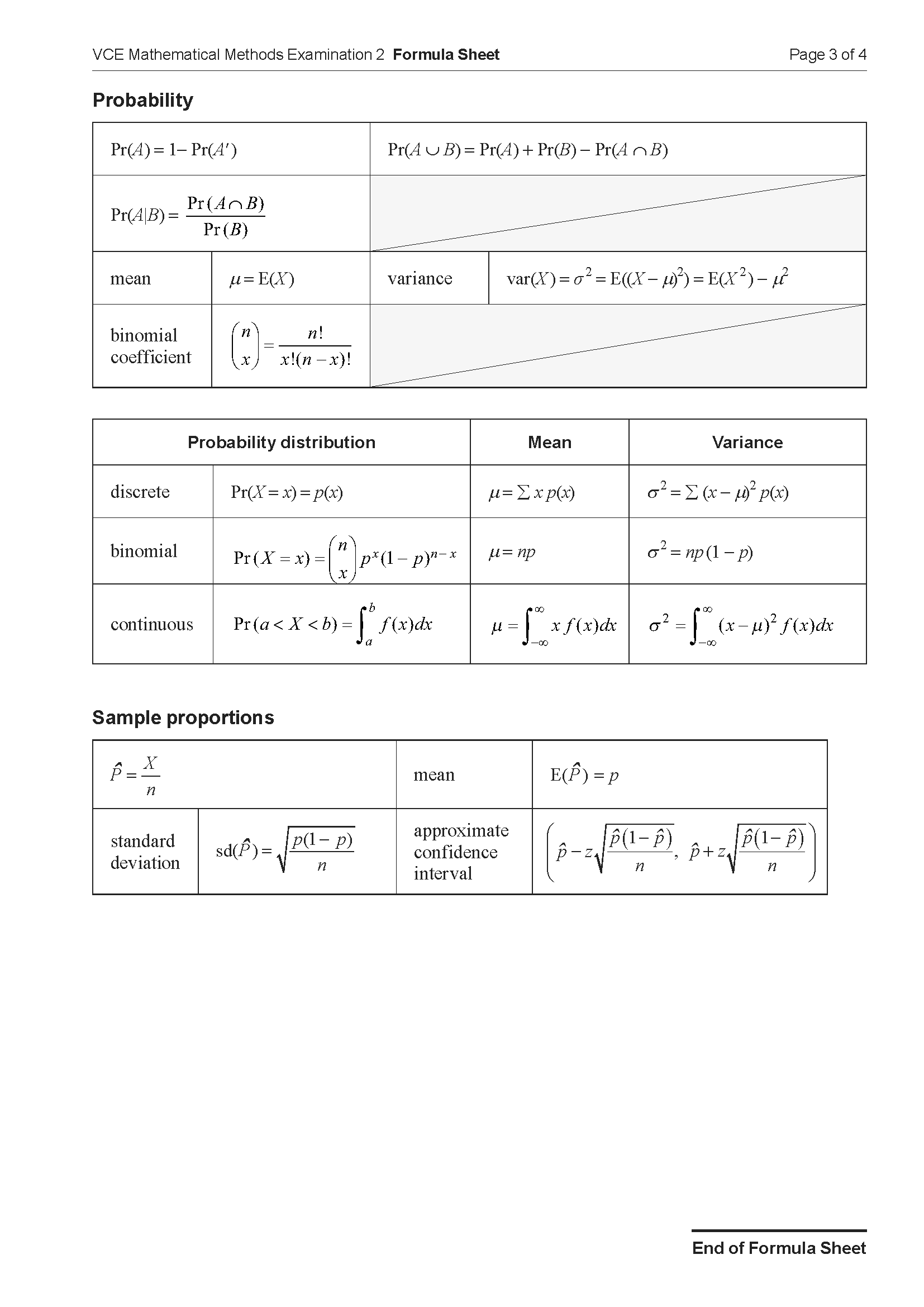
Let \( f : \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R} \), \( f(x) = x(x - 2)(x + 1) \). Part of the graph of \( f \) is shown below.
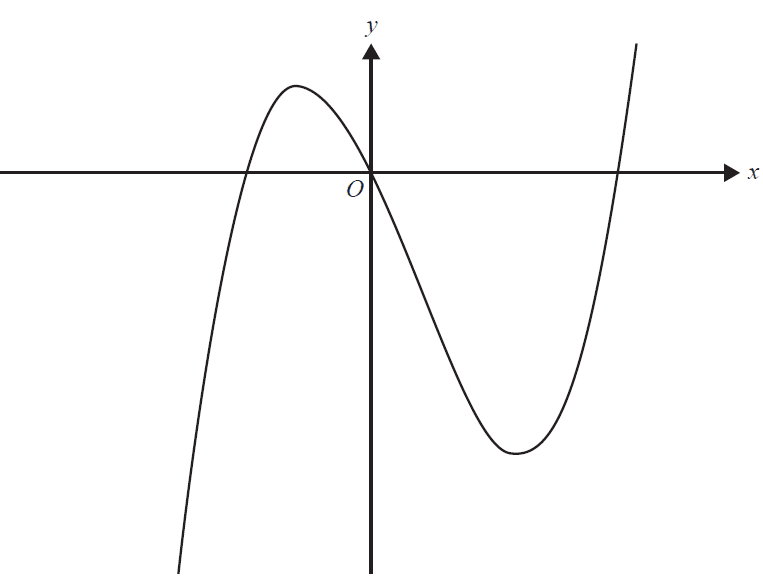
a. State the coordinates of all axial intercepts of \( f \). 1 mark
b. Find the coordinates of the stationary points of \( f \). 2 marks
c. i. Let \( g : \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R} \), \( g(x) = x - 2 \). Find the values of \( x \) for which \( f(x) = g(x) \). 1 mark
ii. Write down an expression using definite integrals that gives the area of the regions bound by \( f \) and \( g \). 2 marks
iii. Hence, find the total area of the regions bound by \( f \) and \( g \), correct to two decimal places. 1 mark
d. Let \( h : \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R} \), \( h(x) = (x - a)(x - b)^2 \), where \( h(x) = f(x) + k \) and \( a, b, k \in \mathbb{R} \). Find the possible values of \( a \) and \( b \). 4 marks
End of examination questions
VCE is a registered trademark of the VCAA. The VCAA does not endorse or make any warranties regarding this study resource. Past VCE exams and related content can be accessed directly at www.vcaa.vic.edu.au