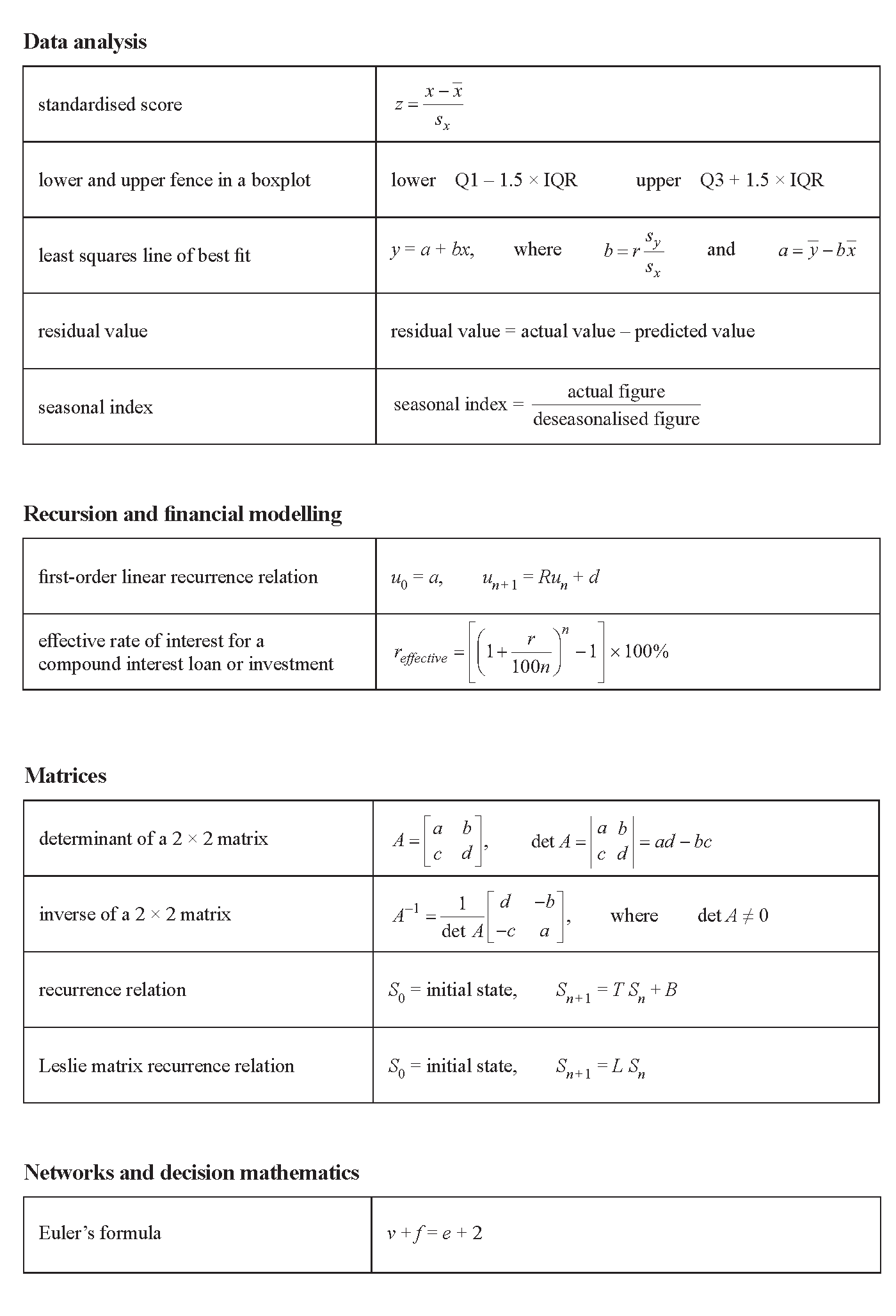
VCE General Maths Recursion and Financial Modelling 2017 Exam 2 Mini Test 1
VCAA General Maths Exam 2
This is the full VCE General Maths Exam with worked solutions. You can also try Mini-Tests, which are official VCAA exams split into short tests you can do anytime.
Number of marks: 9
Reading time: 3 minutes
Writing time: 16 minutes
Instructions
• Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
• Write your responses in English.
• In all questions where a numerical answer is required, you should only round your answer when instructed to do so.
• Unless otherwise indicated, the diagrams in this book are not drawn to scale.
Recursion and financial modelling - 2017 - Exam 2 (Part 1)
Alex is a mobile mechanic.
He uses a van to travel to his customers to repair their cars.
The value of Alex's van is depreciated using the flat rate method of depreciation.
The value of the van, in dollars, after \(n\) years, \(V_n\), can be modelled by the recurrence relation shown below.
\(V_0 = 75\,000, \quad V_{n+1} = V_n - 3375\)
a. Recursion can be used to calculate the value of the van after two years.
Complete the calculations below by writing the appropriate numbers in the boxes provided. 2 marks
\(V_0 = 75\,000\)
\(V_1 = 75\,000 - \) \( = 71\,625\)
\(V_2 = \) \( - \) \( = \)
b. i. By how many dollars is the value of the van depreciated each year? 1 mark
ii. Calculate the annual flat rate of depreciation in the value of the van.
Write your answer as a percentage. 1 mark
c. The value of Alex's van could also be depreciated using the reducing balance method of depreciation.
The value of the van, in dollars, after \(n\) years, \(R_n\), can be modelled by the recurrence relation shown below.
\(R_0 = 75\,000, \quad R_{n+1} = 0.943 R_n\)
At what annual percentage rate is the value of the van depreciated each year? 1 mark
Alex sends a bill to his customers after repairs are completed.
If a customer does not pay the bill by the due date, interest is charged.
Alex charges interest after the due date at the rate of 1.5% per month on the amount of an unpaid bill.
The interest on this amount will compound monthly.
a. Alex sent Marcus a bill of $200 for repairs to his car.
Marcus paid the full amount one month after the due date.
How much did Marcus pay? 1 mark
Alex sent Lily a bill of $428 for repairs to her car.
Lily did not pay the bill by the due date.
Let \(A_n\) be the amount of this bill \(n\) months after the due date.
b. Write down a recurrence relation, in terms of \(A_0\), \(A_{n+1}\) and \(A_n\), that models the amount of the bill. 2 marks
c. Lily paid the full amount of her bill four months after the due date.
How much interest was Lily charged?
Round your answer to the nearest cent. 1 mark
End of Question and Answer Book
VCE is a registered trademark of the VCAA. The VCAA does not endorse or make any warranties regarding this study resource. Past VCE exams and related content can be accessed directly at www.vcaa.vic.edu.au